Essential Windows Protection to minimise service interruption.
Why Windows Recovery Features Matter—And Why Yours Might Not Be Enabled
Whether you're running a PC for daily essentials or managing operations in a work environment, unexpected failures can strike without warning. Fortunately, Windows includes built-in restore features designed to help you bounce back quickly—but many users don’t even realise these tools are switched off by default.
In this post, we'll explore why enabling recovery options is a smart move, especially if you're relying on expert IT support, like us at Optimised Computing. With the right settings in place, service restoration becomes faster and far more reliable.
You might wonder why these safeguards aren’t activated automatically. Some argue for user choice and data privacy—but if your machine handles important tasks, backing up both your files and Windows itself is more than a precaution. It’s essential
These are essential items we have learned to check on our Herefordshire customers while supplying IT support services.
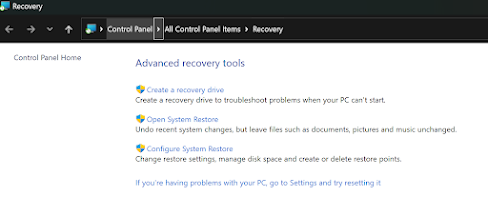
Windows System Recovery.
Under the control panel > Recovery, or typing "create restore point" will lead you to the system protection service. This is an essential item to have switched on and allow it to have at least 25 GB of 25Gb space.
If it's not on, remember when you turn it on to create your 1st restore point.
Windows Registry Backup
The Windows Registry is like the brain of your Windows operating system. It’s a structured database that stores all the settings and configurations for your system, software, hardware, and user preferences.
A registry hive is a major section of this database—think of it as a big folder that holds related settings. Each hive contains keys, subkeys, and values that define how Windows behaves.
Now you know how important it is, it's best to have a backup.
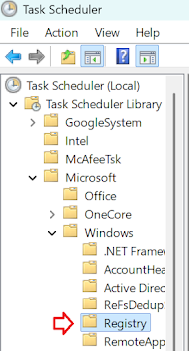
Open "Task Scheduler" and expand "Task Scheduling Library" > " Microsoft" > "Windows" > "Registry"
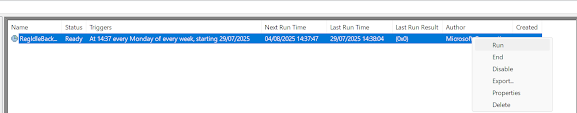
By default, it is not scheduled at all. I recommend you set a weekly trigger. Simply right-click this task and select the "trigger" tab, and set it to one day a week.
Also right click and press "run" to get that 1st backup run asap.
Startup Settings enable a rescue boot menu F8 option
This is an old feature that is disabled by default. However, if it stops working, you won't be able to use the PC to access things like safe mode easily. So, it's best to enable this before you need it.
Open a command prompt as administrator and run the following:
For Windows 8, 8.1 and 10 (old versions) and 11 :
bcdedit /set {default} bootmenupolicy legacy
For Windows 10 version 1903 or later i.e. Windows 11:
bcdedit /set bootmenupolicy legacy
Now press F8 when PC boots and get options to use items like safe mode.
Don’t Get Locked Out: Back Up Your BitLocker Key and Windows Credentials
Using BitLocker encryption and Windows Hello features like face recognition or PIN login is a smart way to secure your device—but without proper backup, it can become a locked door with no key. If your system fails, your password is forgotten, or your biometric login stops working, having access to your BitLocker recovery key and Windows account credentials becomes absolutely critical. Many users assume their device will "just work" in a crisis, but recovery depends on having those essential details safely stored—ideally in a secure cloud vault, password manager, or even printed and locked away. A few minutes of preparation can save hours of frustration and prevent permanent data loss. Trust us at Optimised Computing—recovery is swift when you're equipped for it.
To ensure your data's security, I recommend setting up BitLocker on your Windows PC and saving the encryption key in a safe location.